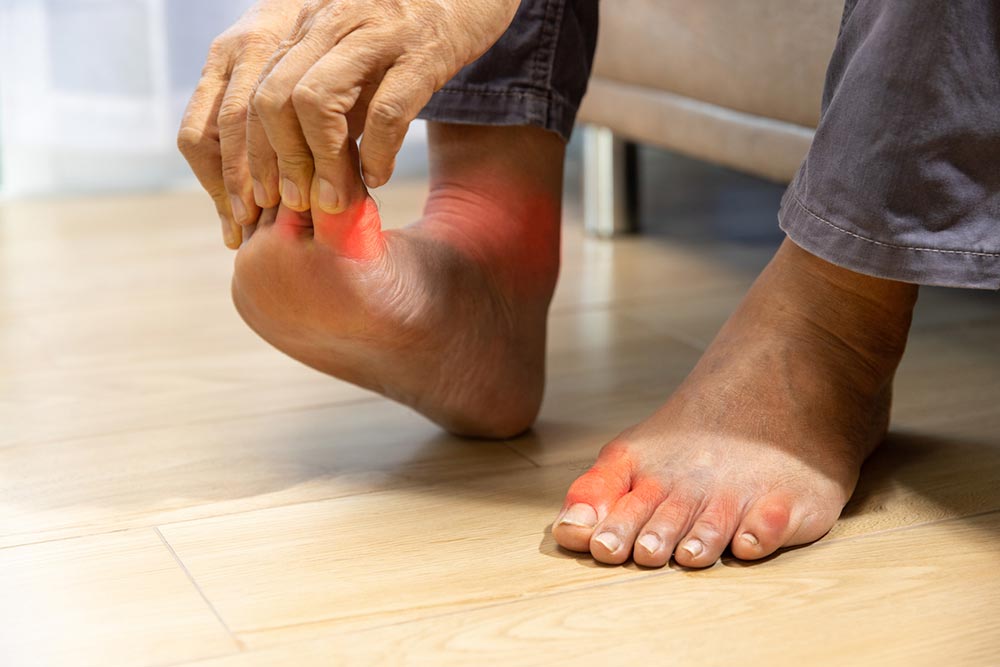
Peripheral neuropathy is a term that refers to damage in the peripheral nervous system, causing pain, numbness, and other symptoms. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders, more than 20 million people of all ages in the United States are estimated to suffer from some form of peripheral neuropathy. However, it is likely that the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy is much more widespread, as many people suffering from this condition have either not been tested for the disease or have not been adequately diagnosed.
The nervous system consists of the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral nerves act as a communication network, allowing for the exchange of information between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that occurs when the nerves that carry messages to and from the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body are damaged.
Peripheral neuropathy can be hereditary or can arise as a result of traumas, infections, metabolic issues, exposure to toxins, and diseases. There are over 100 types of peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms and prognosis vary depending on the type of nerves affected, either motor, sensory nerves, or autonomic nerves. Neuropathy can affect either one nerve (mononeuropathy) or multiple nerves (polyneuropathy).
Causes
Poor diet and excess consumption of alcohol can lead to vitamin deficiencies (particularly of vitamins B-1, B-6, B-12, E and niacin) and stress on the nervous system.
Autoimmune disorder such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other chronic inflammatory syndromes may underlie peripheral neuropathy symptoms.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common causes of peripheral neuropathy, with more than half of diabetes sufferers developing some kind of neuropathy during their lives.
Environmental factors such as exposure to heavy metals or toxic chemicals may contribute to peripheral neuropathy.
Infectious diseases such as Lyme disease, shingles, hepatitis C, leprosy, diphtheria, and HIV can increase risk of peripheral neuropathy.
Physical Traumas can damage nerves directly and result in peripheral neuropathy symptoms.
Other factors may include heritable pathologies, medication side effects, and diseases such as cancer.
Symptoms
Symptoms may range from mild to severe, and sometimes can even be life-threatening. The symptoms depend on the type of nerve fiber that is affected and the type and severity of damage. Some symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may include:
- Weakness
- Numbness, prickling, and tingling
- Acute and chronic pain, especially in the hands and feet, but also in other body parts
- Body movement coordination issues
Diagnosis
Peripheral neuropathy can be diagnosed by performing physiological and neurological diagnostic exams such as:
- Blood tests for signs of vitamin deficiency, liver and kidney dysfunction, and diabetes
- Radiological testing such as MRI and CT scans
- Nerve conduction testing (NCS/NCV) and electromyograms (EMG)
- Muscle and nerve ultrasound testing
- Biopsy
